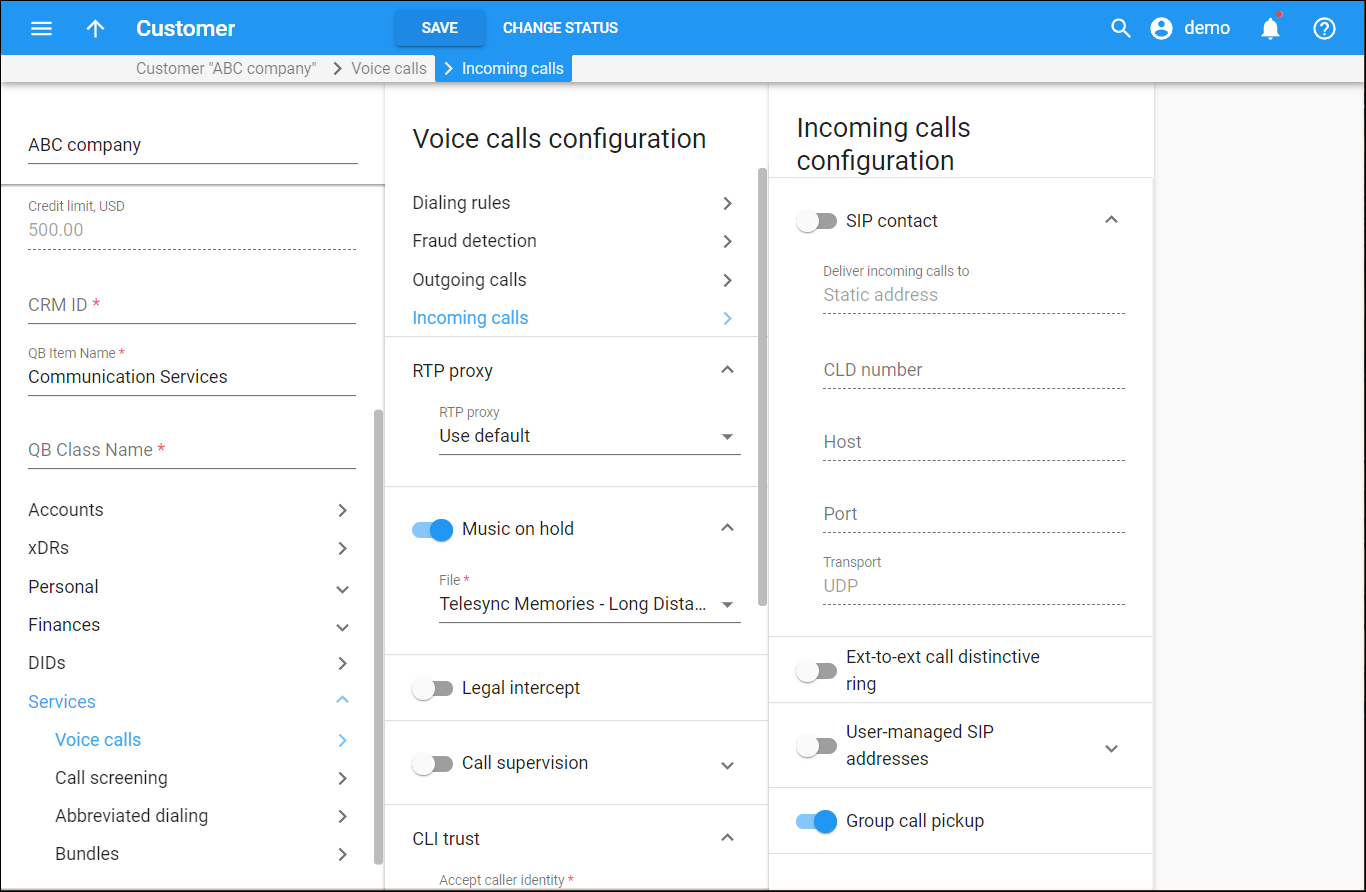
Here you can configure incoming calls processing for the customer. To enable a service feature, turn on the toggle switch. In the expanded menu, define the service attributes.
SIP contact
SIP contact functionality defines how your customer’s PBX registers on PortaSIP and how to process calls to it.
Deliver incoming calls to
Based on the PBX features, define how to deliver calls to it:
-
Static address – if the PBX is located at a static IP address and can’t perform SIP registration, PortaSIP delivers calls to this IP address.
-
Account – the PBX can register only its main phone line and/or receives a dynamic IP address. In this case, PortaSIP forwards all incoming calls to the PBX main phone line, which is provisioned as an account.
CLD number
This is the destination number that calls are routed to when delivered to the PBX IP address. If left blank, the number originally dialed is used as the destination number.
Host
The host name of the PBX. The PBX can be identified by one of the following options:
-
A valid IP address (four numbers separated by points, e.g., 12.34.56.78).
-
A valid domain name (e.g., pbx.example.com).
-
A valid domain name with configured DNS SRV records. In this case, PortaSIP round-robins through them.
Port
Specify the port for the IP address you entered in the Host field.
Transport
The transport protocol used to deliver calls to the PBX. Possible options: UDP, TCP.
Batch
The batch name to which the PBX’s registration account belongs.
Account ID
The ID of the PBX’s registration account.
Ext-to-ext call distinctive ring
Activate the use of a ring pattern different from the default one for incoming calls from phones within the PBX environment.
User-managed SIP addresses
Activate forwarding of customer calls to external SIP proxies using the SIP-URI forwarding mode.
Addresses
Type IP addresses or host names of external SIP proxies here. Use one of the following formats:
-
IP address
-
IP address:port
-
hostname
-
hostname:port
A user-managed SIP address must be unique. Its value length should not be greater than the allowed maximum (255).
Group call pickup
Allow members of the same hunt group to answer each other’s calls by dialing a group pickup prefix.
To fine-tune a group pickup functionality, a customer can organize PBX extensions into pickup groups. Pickup groups are based on hunt groups, e.g., hunt group A with number 2000 can serve as primary pickup group for its extensions 123 and 456. At the same time extension 123 can also belong to hunt group B with number 9999.
In this example, extension 123 has the following pickup options:
-
To pick up an incoming call to hunt group A (its primary pickup group) by dialing only *40;
-
To pick up an incoming call to extension 456 by dialing *40456 (both extensions belong to the same hunt group and have it as their primary pickup group);
-
To pick up an incoming call to hunt group B by dialing *409999 (since extension 123 also belongs to this hunt group).
Note that group pickup must be enabled for the particular hunt group as well.
If there are no primary pickup groups within the PBX (e.g., a small company with only several staff members) any extension can pick up incoming calls of others by dialing only the pickup prefix.