PortaBilling is a versatile tool, and the range of services that can be billed extends far beyond the realm of VOIP. With many VOIP providers also (or primarily) being ISPs, billing Internet access is naturally high on the priority list.
Supported services
PortaBilling supports various billing models for Internet access:
- Fixed bandwidth with unlimited amount of traffic, monthly fee.
- Fixed traffic (quota) at maximum bandwidth, monthly fee.
- Per-megabyte charges at fixed or maximum bandwidth.
- Per-minute charges at fixed or maximum bandwidth.
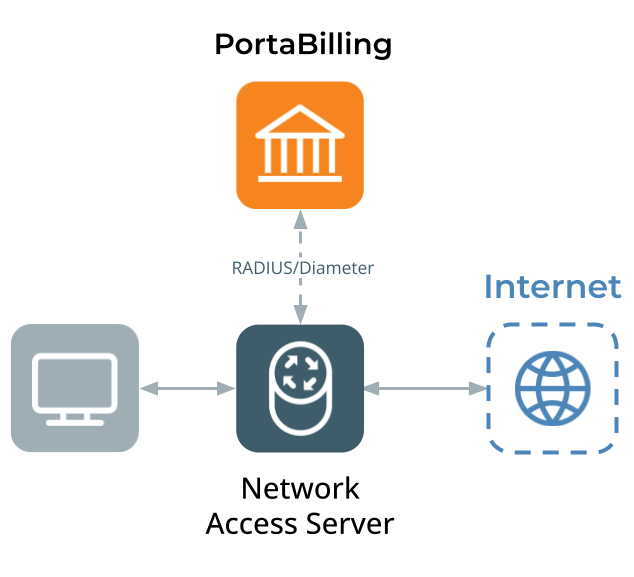
All the models are supported when PortaBilling communicates directly with a Network Access Server (NAS). In this case, it acts as an AAA, including bandwidth/quota control, accumulating usage statistics for user reference, and disconnecting users upon suspension, reached quota or account expiry.
There is also an option to use third-party service controllers (bandwidth/quota control), which are automatically provisioned from PortaBilling. Only first two models are supported in this case.
Provisioning
When a user initiates an Internet session through your NAS (Network Access Server), PortaBilling handles the provisioning of Internet access service. It performs session authorization, verifying the user’s access to the service and determining the maximum allowed data volume. Also, while the Internet session is active, NAS periodically sends usage update requests, and PortaBilling charges the customer based on the consumed data volume and the designated rate code.
- A device (desktop computer with a PPPoE client) connects to a NAS (gateway) requesting that a new session be established. The protocol used for the session between the device and NAS (e.g., PPP or PPPoE) may differ depending on the access technology used, but from the billing perspective, this is irrelevant.
- The NAS forwards account information to PortaBilling for authorization using the Diameter or RADIUS protocol. PortaBilling verifies the account information:
- credentials (“is the account valid?”),
- balance/quota (“does the account have enough funds/traffic quota/minutes?”), and returns the result to the NAS.
Additional information regarding the session (e.g., static IP address) may be returned from PortaBilling to NAS.
- If the account is successfully authenticated, the NAS establishes the session, so the end user can access the Internet.
- While the connection is active, the NAS sends periodic updates about the amount of data transferred within the session, and PortaBilling repeatedly checks the validity and balance of the account (re-authorizes it). If the account has a quota of megabytes/minutes, PortaBilling instructs the NAS to disconnect the session as soon as the quota is reached.
PortaBilling can be used as a backend for any NAS which uses Diameter or a Cisco-compatible RADIUS protocol.
Controlling bandwidth
PortaBilling allows you to control the amount of Internet bandwidth allocated to various types of customers or to even override the default bandwidth policy for an individual customer.
In order to better oversee network utilization, it is very important for an ISP to control the bandwidth available for specific types of customers throughout the day. This includes, for instance, limiting the amount of bandwidth consumed by residential customers during business hours, thus ensuring that business customers receive adequate service; or creating special products for accessing the Internet at maximum speed during nighttime hours, when the network is underutilized.
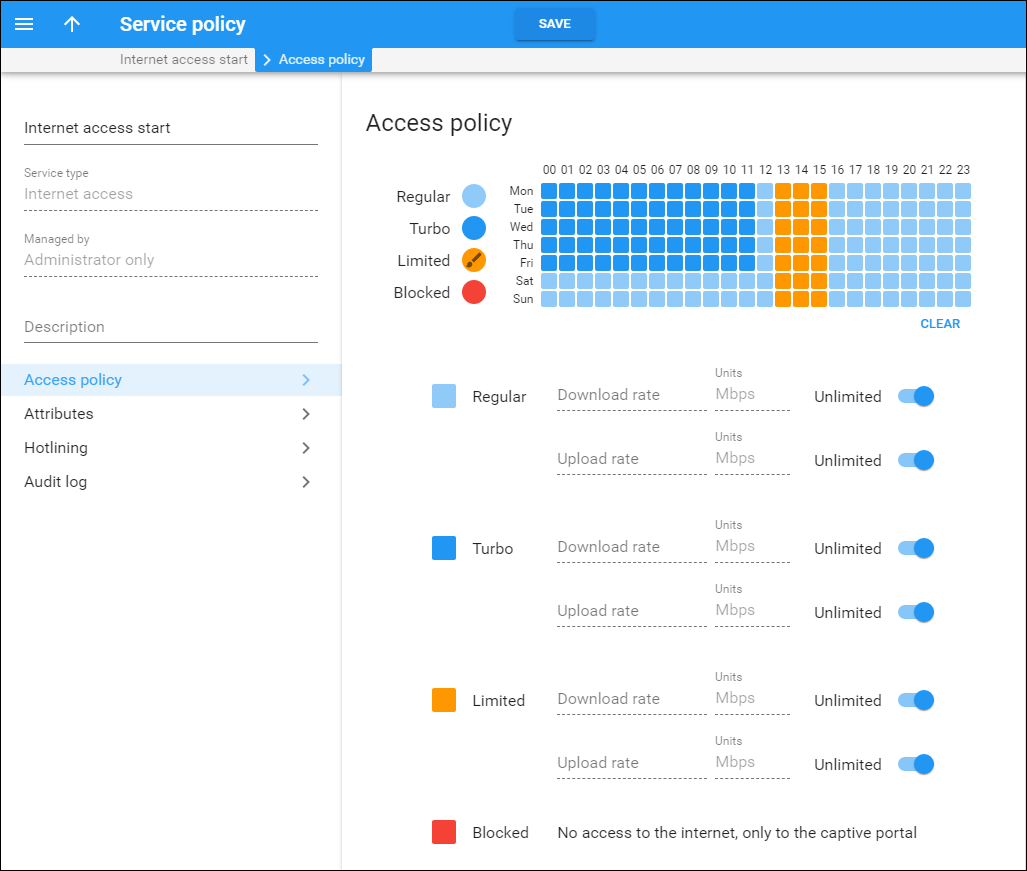
Internet access policy
A policy is a collection of rules and parameters which define how an end user is allowed to access the Internet.
There are four available types of Internet access:
- Regular access (default).
- Turbo access – access during off-peak hours.
- Blocked service (the customer is not able to access the Internet at all).
- Limited access. Typically this is used as an alternative to “blocked” in situations where a customer does not have sufficient funds or failed to pay his last invoice on time. While the customer will not be able to surf the web or download normally, he can still send or receive emails and use the customer self-care interface to submit payment.
Each policy includes:
- A scheduling table, which designates what type of access is used during each time period.
- Specific values for the allowed upload/download speed for each type.
When a new period starts, PortaBilling sends a request to NAS to change the parameters of the current session. This is done using CoA (Change-of-Authorization), for equipment which supports it (in this case the bandwidth re-allocation is done transparently to the end user), or POD (Packet of Disconnect, which terminates the current session).
Rating data
Since Internet access is an “always-on” service, billing is typically done in real time, based on RADIUS update (“keep-alive”) requests received from the NAS; thus many keep-alive requests may be combined into a single xDR. In order to provide detailed information on the charges applied, the contents of each update request are stored in the PortaBilling internal tables, and both summaries and detailed data can be browsed on the PortaBilling web interface.
Data transfer quotas
Data transfer quotas function in a similar way to volume discounts for services such as voice calls. You can define combinations of data transfer thresholds, along with the applicable discounts, e.g., the first 5GB free (100% discount ), after which the customer is charged the normal rate ($0.01/MB).
You also have the ability to adjust the service itself once a threshold is reached, e.g., when the customer exceeds 5GB his download speed will be severely reduced (but he can still use the web, email and the like). If he continues to use the service in an abusive manner, and so exceeds 6GB, the service will be automatically blocked.
Service shutdown
PortaBilling can initiate the disconnection of a session in progress on NAS; for instance, if it is determined that the customer has exceeded the allowed data transfer limit, or if the customer has been suspended due to non-payment. In this case, PortaBilling sends NAS a POD (Packet of Disconnect).
Rating configuration
WiFi
The rate for this special destination will be used to charge your customers for WiFi access service.
NETACCESS
The rate for this special destination will be used to charge your customers for Internet access service such as FTTH, PPPoE or WiMAX.
Routed network provisioning
In cases when a customer needs to purchase an entire IP-network from the ISP, PortaBilling provides the option for configuring the routing information for the customer’s IP-networks on the NAS. To do this, the administrator must indicate the network prefix, the length of the network prefix mask and the gateway IP address in the Routed Networks attribute. This routing information will then be automatically propagated to NAS each time the customer connects.