Administrators can use the role-based security system to control user access to all of the resources in PortaBilling. Access control lies in configuring a role and assigning this role to a user. This ensures that the user can access only those resources they are authorized to see or use.
Roles
Default roles are supplied with PortaBilling – or administrators can create new roles to fit your company needs.
A role can be one of the following types:
- Account – to be assigned to accounts
- CC Staff – to be assigned to customer care support employees
- Customer – to be assigned to retail/reseller customers
- Distributor – to be assigned to distributors
- Representative – to be assigned to representatives
- Reseller – to be assigned to resellers
- Admin – to be assigned to users of the admin interface
- Vendor – to be assigned to your vendors
For now, the Admin, Account and Customer role types are available. Support for other role types will be implemented in subsequent releases.
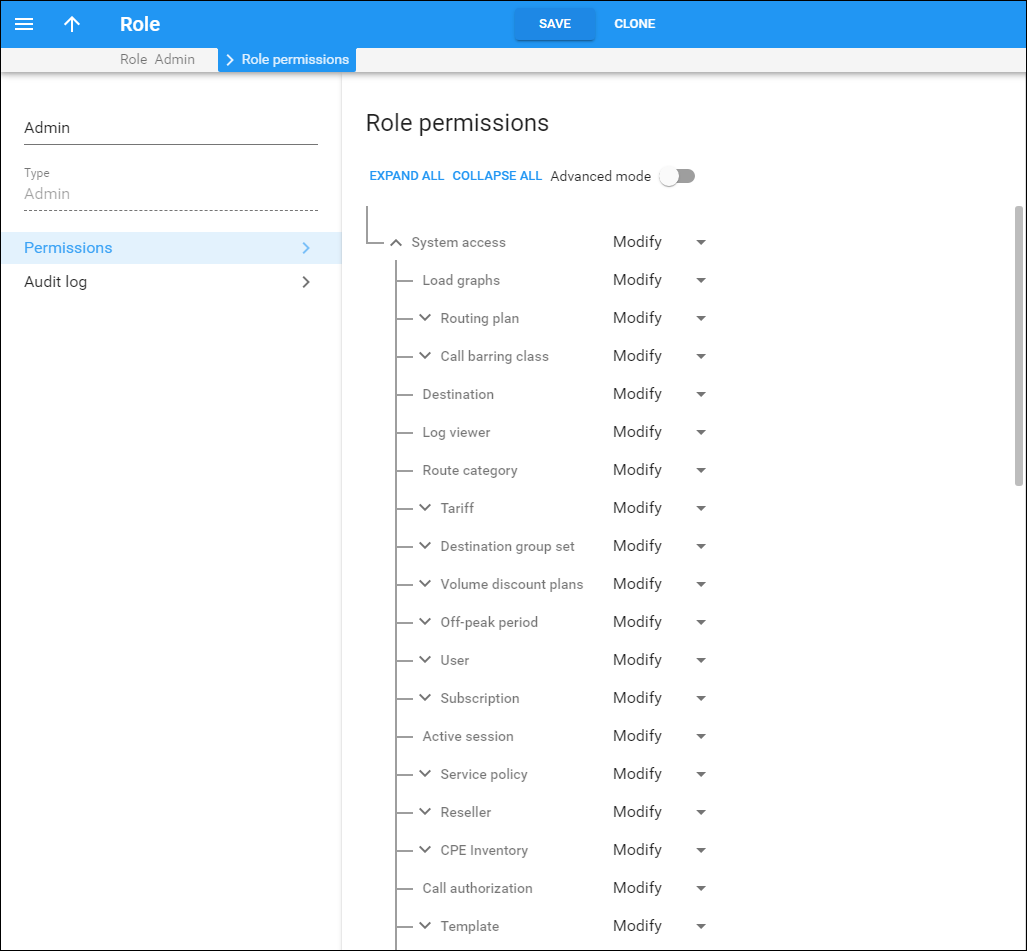
Roles are presented on the web interface as a resource tree wherein root nodes reflect entities in PortaBilling (i.e. customer, account, product, etc.). Second-level nodes reflect entity parameter panels. For example, for a customer entity, it can be the Personal information panel, Invoices and taxation panel, etc.
For each node within the tree, the administrator assigns permissions to define whether an entity or its parameters are available for the user and which actions the user can perform on them. The portal resource tree has a hierarchical structure, that is, lower-level nodes inherit permissions that have been assigned to higher-level nodes.
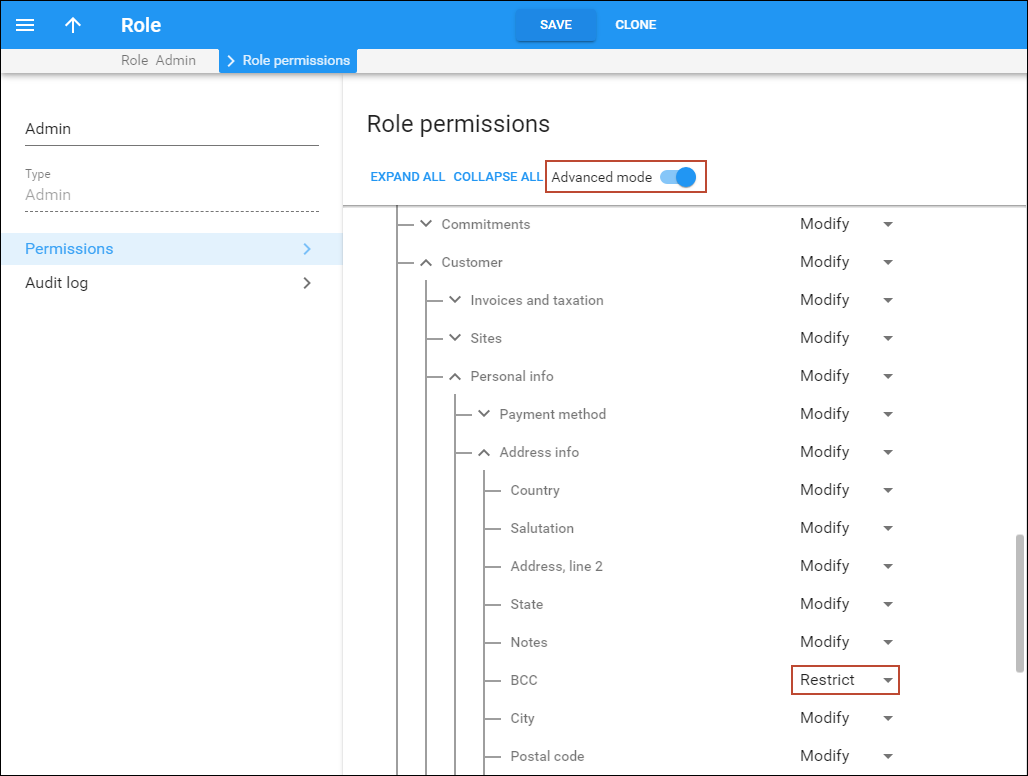
If the administrator needs to hide a certain item on an entity parameter panel (e.g., the BCC field on the Address info panel), they can switch to the Advanced mode. In this mode, the portal resource tree displays a list of items for each entity parameter panel. The administrator then sets the required permission for the corresponding item.
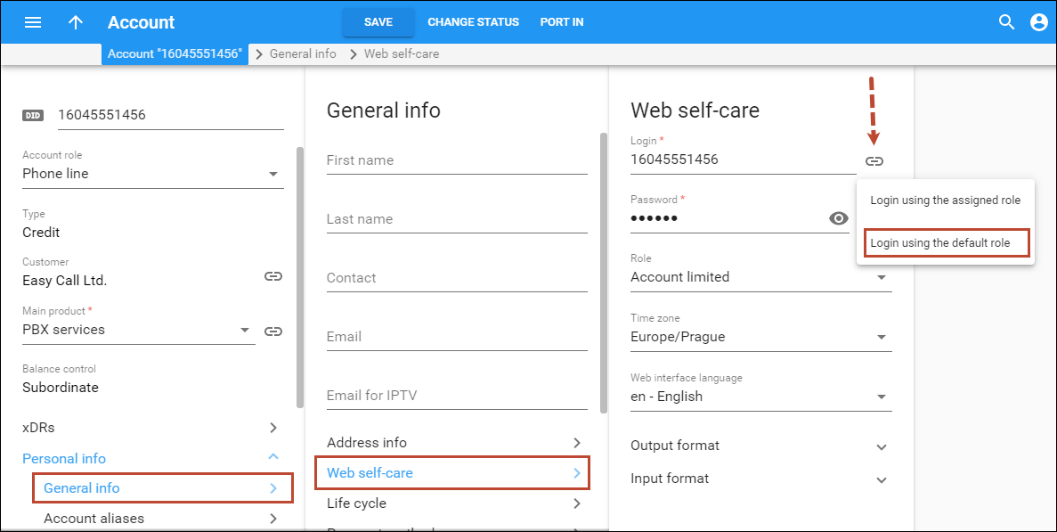
The administrator uses roles to control access to the self-care page for customers/account owners. The administrator can log into a customer self-care page on behalf of the customer, for example, to help with the cloud PBX configuration. If the customer has a custom role assigned to them, the administrator can choose whether to log in with either the custom or the default role.
Permissions
The administrator can assign one of the following permissions in the portal resource tree:
- Restrict – this means that users cannot access the specified resource.
- Read – this permits users to view the specified resource.
- Modify – this permits users to view, update, create and delete the specified resource.
When a user attempts to perform a specific action with a resource (for example, update customer information), PortaBilling checks whether the user has permission for this action. If permission is granted for this action, the user may proceed. Otherwise, the action is not permitted.