Data and database are the most important and critical parts of the system that must be adequately protected.
The only way to eliminate a single point of failure is to have a completely independent copy of a primary database already running on different hardware and ideally deployed at another location. This copy will be used to provide services if the primary database becomes unavailable for any reason.
If your Oracle database is stored only in one SAN (Storage Area Network), then there are two methods to make your system more reliable.
Using one method, you could build a fully redundant architecture using 2 SANs with a double set of switches, etc. It would be possible, but quite expensive.
Using a second method, you could use the Data Guard node to replicate the data from your primary SAN. We suggest this solution because it is cheaper and more effective.
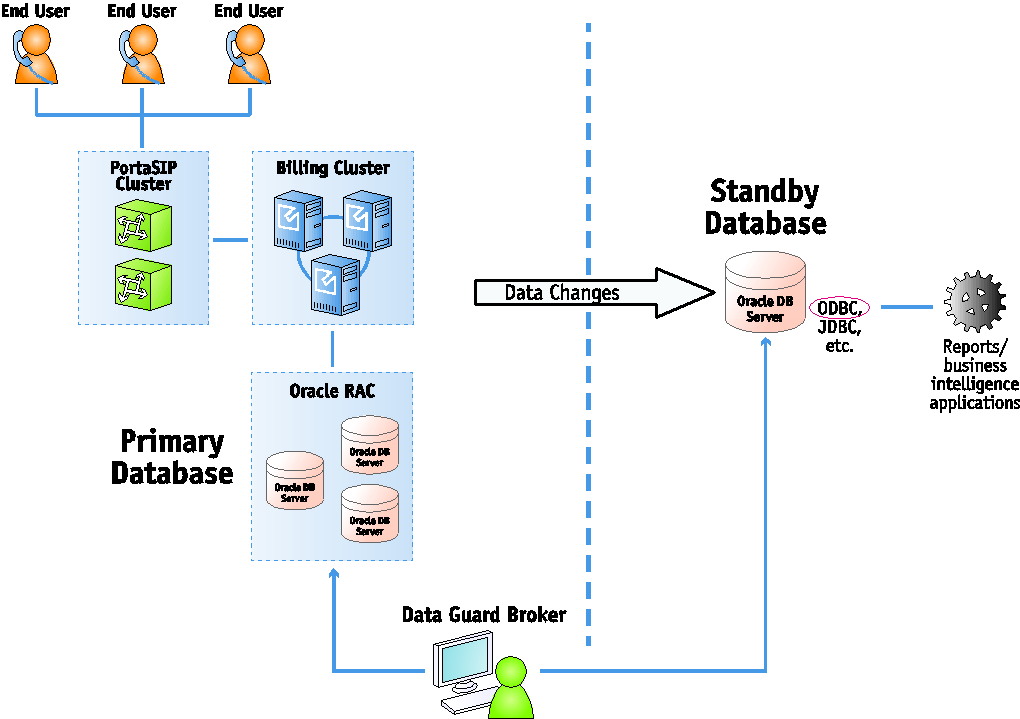
What is the Data Guard node?
Data Guard is a solution from Oracle that creates and maintains database replicas and standby databases. It provides site redundancy (or replication to the secondary site) or database redundancy in the cloud deployments. It is one of the most effective solutions available today for maximizing the availability of Oracle databases and for protecting data from disasters in case of hardware failure and/or data corruption.
Data Guard can also be used as a separate reporting database, where massive data queries can be performed without putting stress on the main database.
Therefore, this is an additional solution to your existing main Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC).
With the Data Guard solution, you are allowed:
- the use of the standby database as the primary if the primary database drops;
- the running of backup jobs on the standby database instead of on the primary one;
- the use of the standby database for the generation of various reports.
How it works
Data Guard maintains a copy of your data in a standby database. It is continuously updated with changes from the primary database. It validates all of the changes before they are applied to the standby database, preventing data loss caused by corruption.
The standby database can be located in the same city or even in the same building with the main data center. If the primary database becomes unavailable (e.g., due to hardware failure), it is possible to switch to the standby database, thus minimizing the downtime associated with the outage and preventing any data loss.
Additionally, if the primary database detects a block corruption event, it automatically attempts to repair the corrupted block in real time by obtaining an uncorrupted version of the same block from a standby database. Therefore, block corruptions are transparently resolved by the administrator.
Furthermore, the same Data Guard node solution can be used when your standby database is located at a remote secondary site, miles away from your main data center.
Benefits from using the Data Guard node
By implementing the Data Guard node solution, you obtain the following benefits:
- Rapid recovery after a SAN crash or data corruption – the switchover and failover capabilities of this solution allow role reversals between primary and standby databases. This increases the reliability of your services by increasing data storage reliability.
- Additional data protection – a guaranteed up-to-date binary copy of the primary database.
- Reduction of the primary database workload – the standby database can be used for other tasks such as backup operations, reporting, summations, queries, data mining, etc.
- Cost reductions – the replica database can be run on a normal server and does not require an additional SAN.