There are two types of passwords in PortaBilling:
-
Web interface password. This password is used in combination with a login to authenticate a user (e.g., admin, end user) who gains access to their web self-care interface.
-
Service password. This password is used to authenticate all calls made using the account. It is also used to register a SIP account on a SIP phone/softphone. Only accounts have this password. In the PortaBilling API, a service password corresponds to a h323_password attribute.
To secure password storage, hashing and encryption mechanisms are used. These measures protect users’ passwords in case an unauthorized person obtains access to the database.
Set requirements for web interface password complexity
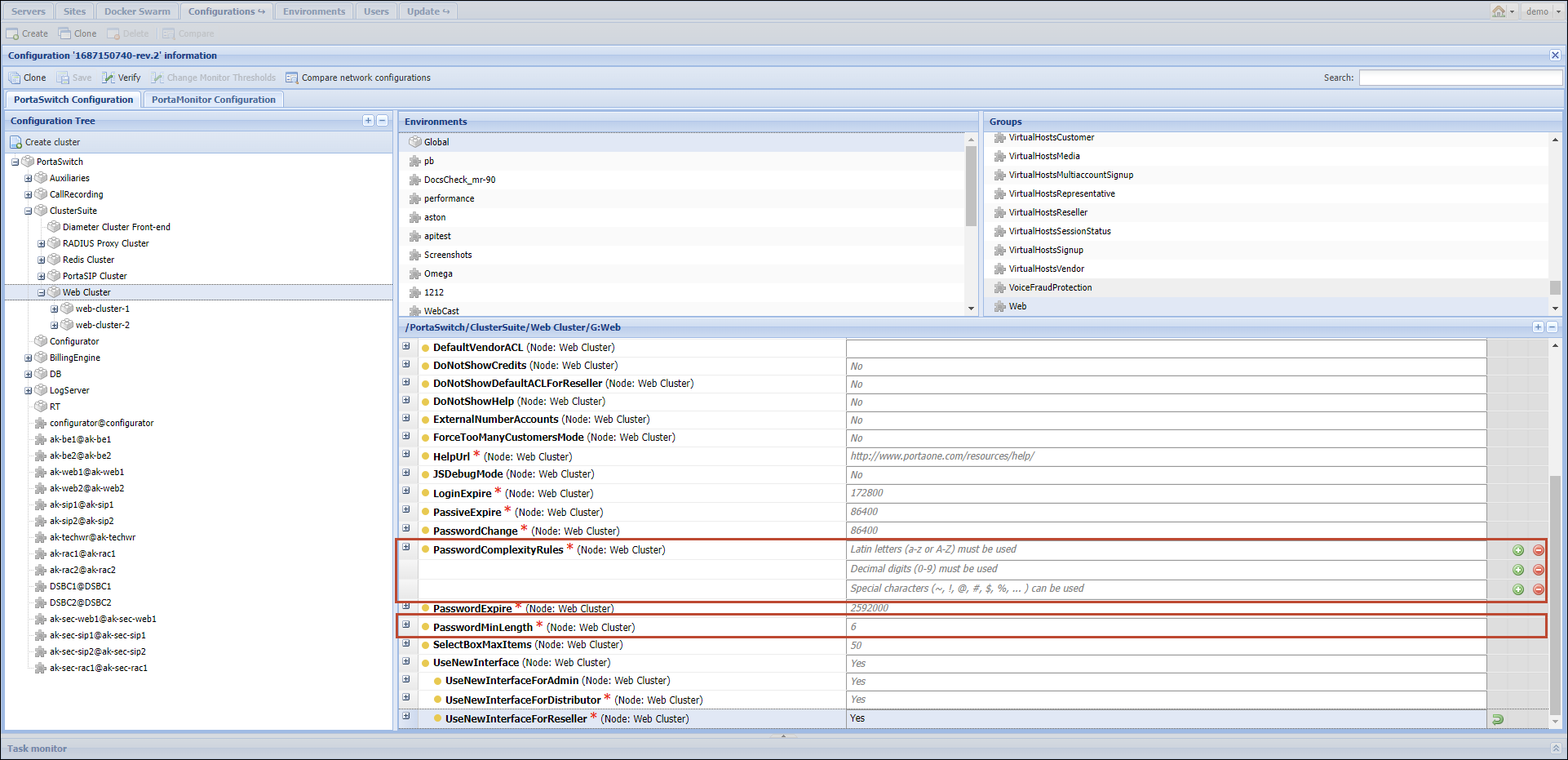
To improve the password security for administrator’s and self-care web interfaces, you can configure password complexity requirements, such as minimum password length, on the Configuration server.
These conditions can be set by specifying the following options:
- Web.PasswordComplexityRules – specify whether a password can or must include:
- Latin letters (a-z or A-Z)
- Decimal digits (0-9)
- Lowercase letters (a-z)
- Uppercase letters (A-Z)
- Special characters (~, !, @, #, $, %, ... )
By default, a password must include Latin letters and decimal digits, and can include special characters.
- Web.PasswordMinLength – specify the minimum password length. The default value is 6.
Hashing passwords
Hashing performs a one-way password transformation. A password is turned into a hash value (data chunk of a fixed size). This hash value is unique and stored in a database. When a user attempts to log in, the system takes the password entered and performs a similar one-way hash. Then the system compares the hash value that was provided with the database hash value. If they match, the user logs in successfully. It is impossible to transform a hash value into initial symbols. Hashing is not reversible. Highlights:
- All users that are created via the PortaBilling web-interface (My company > Access control > Users), e.g., users with root permissions, administrators, operators.
- CC staff created by resellers. For example, customer care support employees.
- Web interface passwords are hashed only.
- Passwords are hashed by default. Hashing cannot be turned off.
- Hashed passwords cannot be converted to plain text.
Encrypting passwords
Encryption is a two-way password transformation. It means that a password can be decrypted to initial symbols. Users with ACL/a role that permits them to obtain passwords, can obtain them in plain text. For example, an administrator can put an account password into plain text by using the get_account_info API method.
Encryption uses a passphrase along with salt. The passphrase is a key used for encrypting or decrypting passwords. Salt is random data used to randomize output after encryption. Salt complicates the process of deciphering an encrypted password since each salt value is unique, even for two identical passwords.
Passwords encrypted with salt are stored in a database while a passphrase is stored on several servers. Encrypte passwords and a passphrase are stored in different places which makes them secure. For this reason, it is difficult to crack these passwords, even if an attacker obtains access to the database.
An administrator can change a passphrase with a CLI utility. For more information, contact PortaOne support. During this procedure, an old encryption passphrase is replaced by a new one. This requires decryption-encryption and an update for all passwords in the database. During this procedure, account owners can continue using their services as usual; i.e. there is no downtime. Highlights:
- Passwords are encrypted for the following entities:
- Accounts
- Customers
- Resellers
- Distributors
- Representatives
- Both web interface passwords and service passwords are encrypted.
- The passwords of vendors and representatives are always stored in plain text.
- Encryption is enabled by default. It can be turned off on the Configuration server (Security.EncryptPasswords option).
- A passphrase can be changed via a console utility.
- Users with the right ACL/role permissions can obtain encrypted passwords in plain text.
Password expiration
By default, passwords that are used to log in to the admin, reseller web interface, or self-care portals expire in 30 days. After this period, users are prompted to change their password. Users with expired passwords do not have access to any features on the portals.
You can change the default period for password expiration using the Web.Password_expire option on the Configuration server web interface.
Note that if your external portal does not yet include a “Password reset” feature that invokes the Session/change_password method, and you want your users to have full access to portal features, it can be beneficial to avoid a forced password change. To do that, set “0” for the Web.PasswordExpire option on the Configuration server web interface. With this option, the passwords of all the users will never expire, and they can continue logging in with their expired passwords and working on the portal.
Storing admin web password in browsers
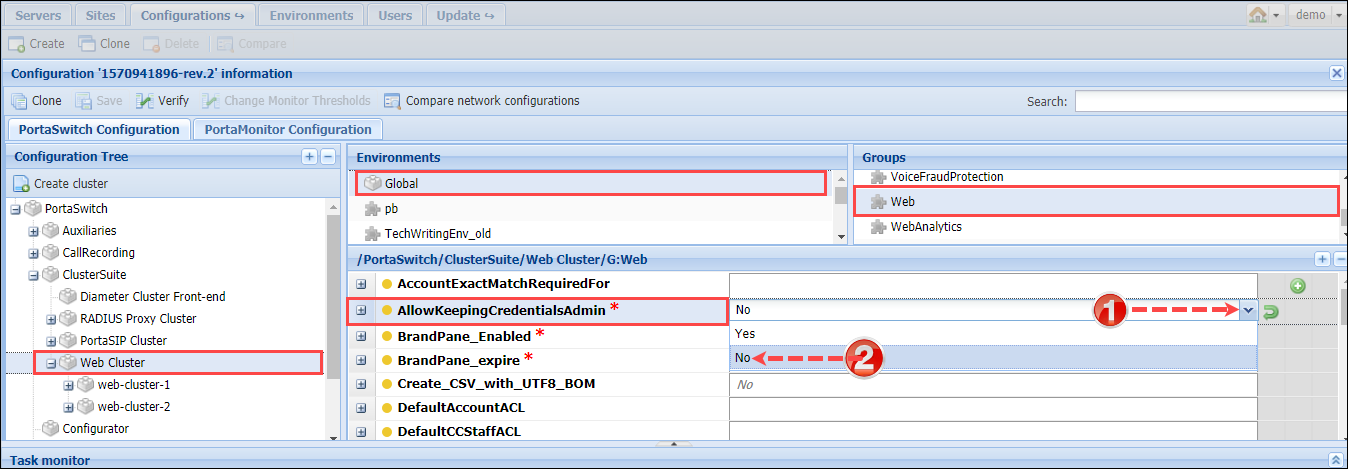
Administrators often store credentials to PortaBilling web GUI in password managers. The best security practice is to store the passwords encrypted. However, a browser’s password manager does not encrypt passwords by default and those passwords might be stolen (e.g., by means of malicious software, when the device is lost, etc.). To ensure the optimum security in PortaBilling, you can disable storing credentials in browsers’ password managers. Thus, every administrative user must specify their login and password every time they log in to PortaBilling. To disable storing credentials, set AllowKeepingCredentialsAdmin option to No on the Configuration server.