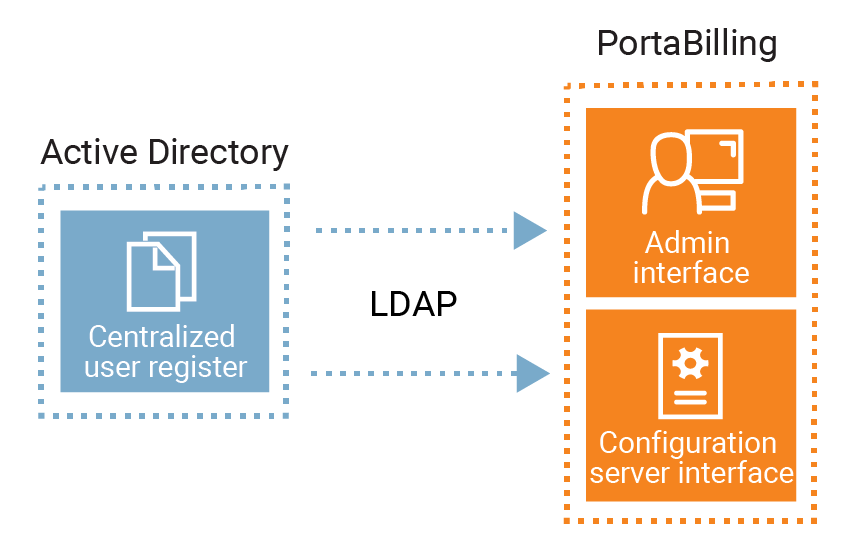
The Microsoft Active Directory (AD) is a directory service that enables service providers to manage users within their entire infrastructure from a single location. An AD administrator can create/block/delete user records, manage their details, and provide access to all corporate resources (for example, Microsoft SharePoint, Microsoft Teams, or Odoo CRM) via the AD. Thus, an AD administrator can quickly enable access for new employees and instantly block access to all corporate resources when somebody leaves the company. This saves significant time on user management and it improves infrastructure security.
An AD administrator can create user records in AD to manage access to:
- PortaBilling web interface
- The Configuration server web interface
Therefore, users can access the PortaBilling and Configuration server’s web interface in addition to other resources using a single set of credentials. This simplifies the login process and reduces the risk of losing or forgetting multiple passwords.
To communicate with the AD, PortaBilling supports the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). The (LDAP) user password is stored in the AD database. Thus, the user is authenticated in PortaBilling through the AD. The LDAP is also used for data synchronization (user name, login, password, email, country, role, expiration date) between the AD and PortaBilling.
This is how it works:
- The AD administrator creates a user record in the AD that is then automatically created in PortaBilling.
- The user logs in to the PortaBilling web interface using their LDAP credentials provided by an AD administrator.
- PortaBilling sends an authentication request to the AD via the LDAP.
- The AD verifies the user login and the LDAP password.
- Access to the PortaBilling web interface is provided according to the user access role.
- When an AD administrator changes a user’s access role or user details, the data is synchronized with PortaBilling via the LDAP.
- When the AD administrator deletes the PortaBilling user record from the AD, it is automatically deleted from PortaBilling, too.
Let’s say a service provider hires a new employee, David. David is an accountant and needs read-only access to PortaBilling. The AD administrator opens the AD and creates a new user record with the Helpdesk access role. The AD sends the user data via the LDAP and creates a new user record in PortaBilling. Now David can log in to PortaBilling using his LDAP password. In a few months, when David leaves the company, the AD administrator blocks David’s user record in the AD. The AD then synchronizes with PortaBilling and blocks the user record there. Thus, David’s access to PortaBilling is blocked.
Specifics
- To log in to PortaBilling or the Configuration server web interface, the AD administrator must create a user record in the AD first.
- The AD stores the user data (e.g., login, password) and authenticates the user’s access to PortaBilling via the LDAP.
- Only an AD administrator can create/delete/block the PortaBilling user record and manage the mandatory user fields:
- Name/Surname
- Login
- Password
- Role
- Country
- Company
- Expiration date
- User details specified in the AD are read-only in PortaBilling.
- By default, data in PortaBilling synchronizes every 10 minutes with AD. You can change the synchronization frequency on the Configuration server.
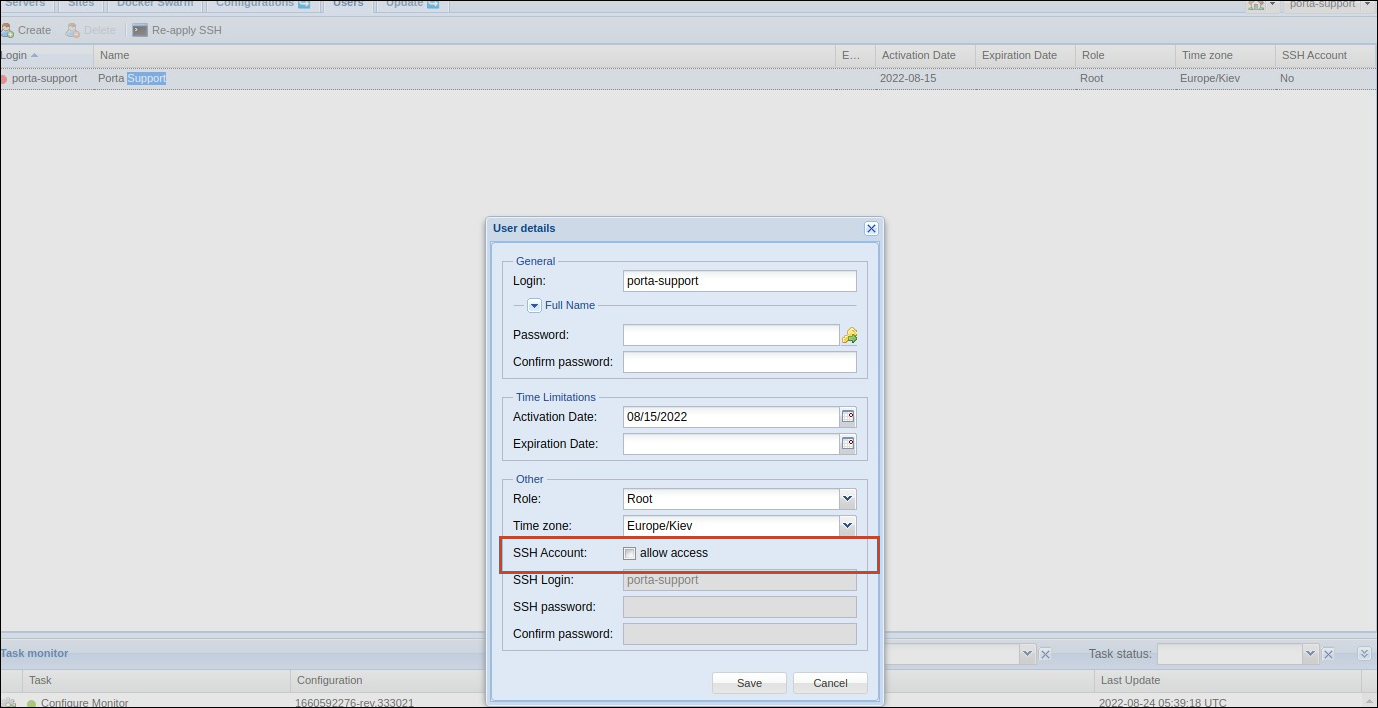
- Access to the Configuration server via SSH is disabled by default. You can enable access on the Configuration server: open the Users tab > open a specific user detail > select the Allow access checkbox next to the SSH Account field.
Integration with the Microsoft Active Directory allows service providers:
- to enable users to access their corporate resources with a single set of credentials, and
- to manage PortaBilling users within a centralized user register. This reduces significant time on user management for company administrators.
Contact the PortaOne support team to configure PortaBilling to interact with the Microsoft Active Directory.
Redundant LDAP servers for the Microsoft Active Directory
The LDAP server is used to authenticate AD users in PortaBilling and to synchronize data between the AD and PortaBilling.
You can specify multiple LDAP server addresses to provide redundancy. Thus, if the first LDAP server is down for some reason, the other server is used for AD user authentication. This ensures that AD users can access PortaBilling or the Configuration server web interface without interruptions.
For example, David, an AD user, logs in to the PortaBilling web interface using his LDAP credentials. PortaBilling sends an authentication request to the AD via the LDAP. The first LDAP server (1.1.1.1) is unavailable, thus, the system connects to the second LDAP server (2.2.2.2). The AD verifies the user login and the LDAP password. David can now access the PortaBilling web interface.
Redundant LDAP servers provide AD users with stable access to PortaBilling and Configuration server web interfaces.
Find the detailed description on how to configure PortaBilling to interact with the Microsoft Active Directory in the How to chapter of the PortaSwitch Configuration Server Web Reference Guide.