Configure incoming call processing for an account and define the values of service attributes for an account.
Unified messaging
This allows the account owner to access the unified messaging system.
Turn on the toggle switch to allow end users to access their voice mailbox and/or redirect incoming calls to voicemail.
Mailbox limit, MB – specify the maximum disk space allowed for user mailboxes. In this way you control overall disk space availability.
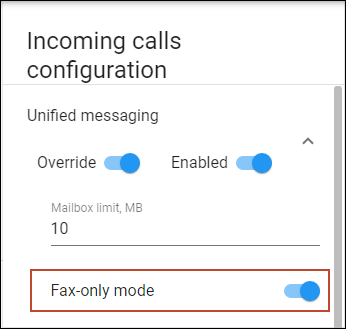
Fax-only mode
This allows you to configure a phone line as a dedicated fax machine.
When the Fax-only mode is enabled (e.g., for an account that represents a DID number), every call to this number is answered with “start fax tones”, which indicates that it will only receive fax messages. The phone line then serves as a dedicated fax line, and emulates the behavior of a legacy fax machine.
External voicemail
If you operate as an MVNO with PortaSIP integrated to the IMS core as a telephone application server, you can redirect your users’ incoming calls to the voicemail service of your host MNO. When a user doesn’t answer an incoming call, PortaSIP sends the call to the IMS with the request to forward it to the voicemail. The IMS terminates the call and launches the voicemail application.
To redirect user calls to the external voicemail service, you must include the out_hdr_history and append_incoming_headers attributes in the service policy for the outgoing vendor connection that represents the IMS.
Access number – specify the access number of the external voicemail service. Users dial it to manage their voice mailbox.
Caller ID (CNAM) lookup
This allows users to see the actual caller name retrieved from the CNAM database, in addition to the phone number. You must be integrated with the CNAM provider and configure the CNAM lookup on the Configuration server. Then, during incoming calls, PortaSIP sends CNAM requests and retrieves the caller ID. Currently, PortaSwitch is integrated with OpenCNAM, which supports numbers from the USA and Canada.
Call waiting
Call waiting alerts users of one or more calls that await connection during a current conversation. Users can answer the second call while the first one is put on hold.
Auto attendant
Auto attendant is an automated voice service in which callers are automatically transferred to an extension without operator interference. When enabled for an account, PortaSIP routes all incoming calls to the auto attendant, even if the Unified messaging service is also enabled.
Default answering mode
Specify the method of processing incoming calls to this account.
Timeout, sec – this defines how long the IP phone will ring before a call goes to follow-me numbers (if any) or voicemail.
SIP contact
SIP contact functionality defines how your customer’s PBX registers on PortaSIP and how to process calls to it.
Deliver incoming calls to – define whether the PBX address for delivering incoming calls is taken from the PBX registration account or specified directly in the Static address field:
-
Static address – if the PBX is located at a static IP address and can’t perform SIP registration, PortaSIP delivers calls to this IP address.
-
CLD number – this is the destination number that calls are routed to. If left blank, the number originally dialed is used as the destination number.
-
Host – this is the host name of the PBX that calls are routed to. An PBX can be identified with a valid IP address (four numbers separated by points, e.g., 12.34.56.78) or a valid domain name (e.g., pbx.example.com).
-
Port – the PBX port for SIP communication to which requests are sent.
-
Transport – the transport protocol (either TCP or UDP) used to deliver incoming calls.
-
-
Account – the PBX registration account. Select this option if a customer’s PBX is located at a dynamic IP address and can register only the main phone line (provisioned as the registration account in PortaBilling) on the PortaSIP server.
-
Batch – specify which batch the registration account belongs to.
-
Account ID – select the account ID from the list.
-
Ext-to-ext call distinctive ring
Activate the use of a ring pattern that is different from the default for incoming calls from phones within the PBX environment.
SIP dynamic registration
This allows IP phone (SIP user agent) registration with a specific account. When an incoming call arrives, the IP phone registered with the account’s credentials rings. By default, SIP dynamic registration is enabled for a product, and all accounts with this product inherit this setting.
If incoming calls should not ring on an IP phone, you can prevent IP phone registration for such accounts by disabling this option (directly on the account page or via the product).
For example, the calls to Auto Attendant should be routed to the IVR and are answered automatically, and no IP phones must be registered with an account configured as Auto Attendant. If an IP phone is registered with such an account by mistake, the calls will be routed to the IP phone. To avoid this, the administrator can explicitly forbid IP phone registration with Auto Attendant.
Turn off the SIP dynamic registration toggle switch for an account configured as Auto Attendant.
User application
Allow the use of custom IVR applications with this account owner to manage incoming calls and automate the user’s workflow. The custom IVR application communicates with PortaSwitch via the call control API.
For example, let’s say your customer, a visa processing center, develops an IVR application to announce the visa status to callers. You provision this application on the Voice applications panel and enable the User application functionality for the customer’s account. When a caller dials the access number, PortaSwitch sends the call to the IVR associated with that customer. The IVR prompts the caller to enter their registration number, then retrieves their visa status from the external database and plays the corresponding IVR message.
Max numbers – specify the number of access numbers (DID numbers) that can be used by customer’s accounts. For instance, your customer, a visa processing center, has 3 accounts configured in PortaSwitch. If the Max numbers is set to 5, then only up to 5 access numbers can be requested for every account.
Present caller info
Allow end users to see caller information for incoming calls.
Call forwarding
This defines how to process incoming user calls.
Maximum forwards – this specifies how many forwarding destinations are concurrently active at any given moment. It doesn’t limit the total number of phone numbers entered into the forwarding list by the user. For example, a user may have a list of 20 numbers, each active in its own time period, some temporarily turned off, etc. When call forwarding is done, PortaBilling computes a list of numbers which may be used at that moment, and chooses only the first N in the list, where N is the number specified in Maximum forwards.
This option is active only when call forwarding is enabled.
Forward by DTMF – users can transfer incoming calls forwarded to their mobile phones from their PBX extensions by dialing DTMF tones on their mobile phone. Users stay on the line until the other party picks up.
For example, if a user receives a call to his mobile phone and needs to transfer it to his colleague at extension 1002, he dials *661002#, and when his colleague confirms that she is free to take the call, he hangs up.
Call forwarding – select a forwarding mode to process incoming calls:
-
Follow-me allows users to define multiple destinations for call forwarding, each of which is active in its own time period. Users can also specify that multiple numbers be tried one after another, or that they all ring at the same time, or that they are tried, percentage-wise, depending on the total number of incoming calls.
-
Advanced forwarding provides extra options for the follow-me mode. Users can select the SIP proxy to which PortaSIP routes their calls
-
Forward to SIP URI allows end user to enter a forwarding destination as a phone number and an IP address in the format CLD@IP or CLD@domain. PortaSIP round-robins through DNS SRV records if they are configured for the specific domain. This mode is useful for when calls are forwarded to an external SIP proxy.
-
Simple forwarding forwards all calls, unconditionally, to a single phone number pre-defined by the user.
Click the forwarding settings link to specify the forwarding details.
Call screening
Call screening allows users to configure how their incoming calls should be handled according to predefined rules, e.g., redirect all calls to voicemail during non-working hours, yet allow calls from a boss to always come through.
To enable call screening, turn on the Enabled toggle. To override the call screening configuration you provide to the account via the product, turn on the Override toggle.
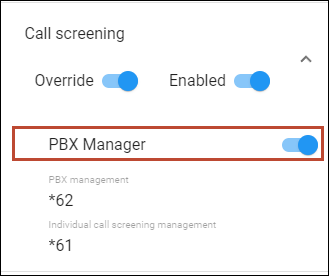
PBX manager
Turn on the PBX manager toggle to authorize the user to change the call processing mode not only for their own extension, but also for all PBX extensions at once.
To act as a PBX manager and manage the call screening settings for all PBX extensions, an authorized user should dial the service code shown in the PBX management field, e.g., *62.
To change the call processing mode for their own extension, a user should dial the service code defined in the Individual call screening management field, e.g., *61, or manage these settings through the self-care portal.
Perform caller verification
Enable this feature to configure the incoming call verification in PortaBilling.
Ringback tone
Replace ordinary ringback sounds with custom tones (e.g., music) here.
File – upload the file with custom ringback tones that callers hear instead of default sounds.